Installing Nvidia Tao and DeepStream Theory
Nvidia Tao Tutorial
 |
|---|
| why DeepStream in the first place? |
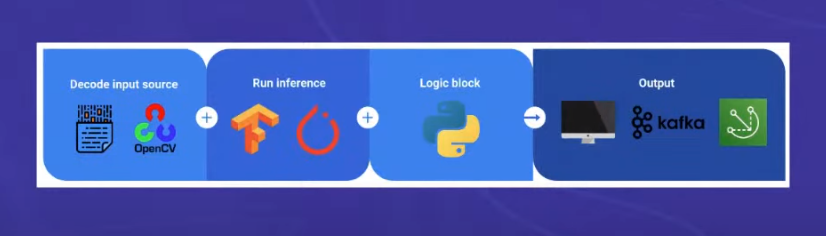
Introduction
Decode Input source: OpenCV is a go to choice for operations on images. It is a library of programming functions mainly aimed at real-time computer vision. It is used for all sorts of image and video analysis, like facial recognition and detection, license plate reading, photo editing, advanced robotic vision, optical character recognition, and a whole lot more.
Run Inference: Pytorch for researchers and Tensorflow for production. this is the brain of the system. It is a deep learning framework that is used to build and train neural networks. It is a free and open-source software library for data manipulation and analysis. It is used for a wide range of tasks including data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing.
Logic Block: its the logical code you write to connect things, mostly use python since its easy to learn and implement stuff.
Output: Displays, IOT services, AWS Servers could be anything.
One things is none of the above are accelerated except the inference block. This is because a module does operations on CPU and a few does it on GPU, the bottleneck part takes time and makes your system slow.
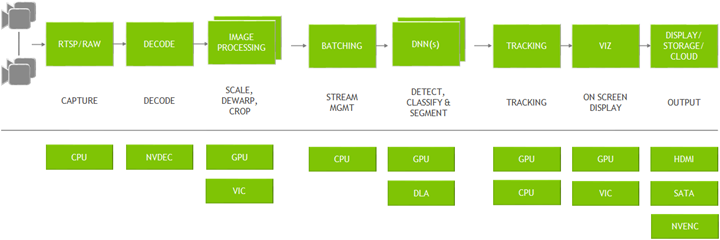
Deepstream Module
|  |
|:–:|
| Blocks of Deepstream Module |
|
|:–:|
| Blocks of Deepstream Module |
CCTV generate feed called RTSP, sends data over that protocol, networks operations are done on CPU Decoders generate the information, images.jpg to numpy arrary for pythonists using OpenCV. Image processing stuff, like cropping, resizing, etc are done on CPU/GPU, this is where the bottleneck is. Batching is always done on gpu. DNN( deep neural nets) are done on GPU/ DLA(deep learning accelerator) which is a part of GPU. DLA is similar to TPU. Tracking for object detection is done on GPU/CPU. visuvalization, When you wnated to draw on an image, GPU takes care of it.
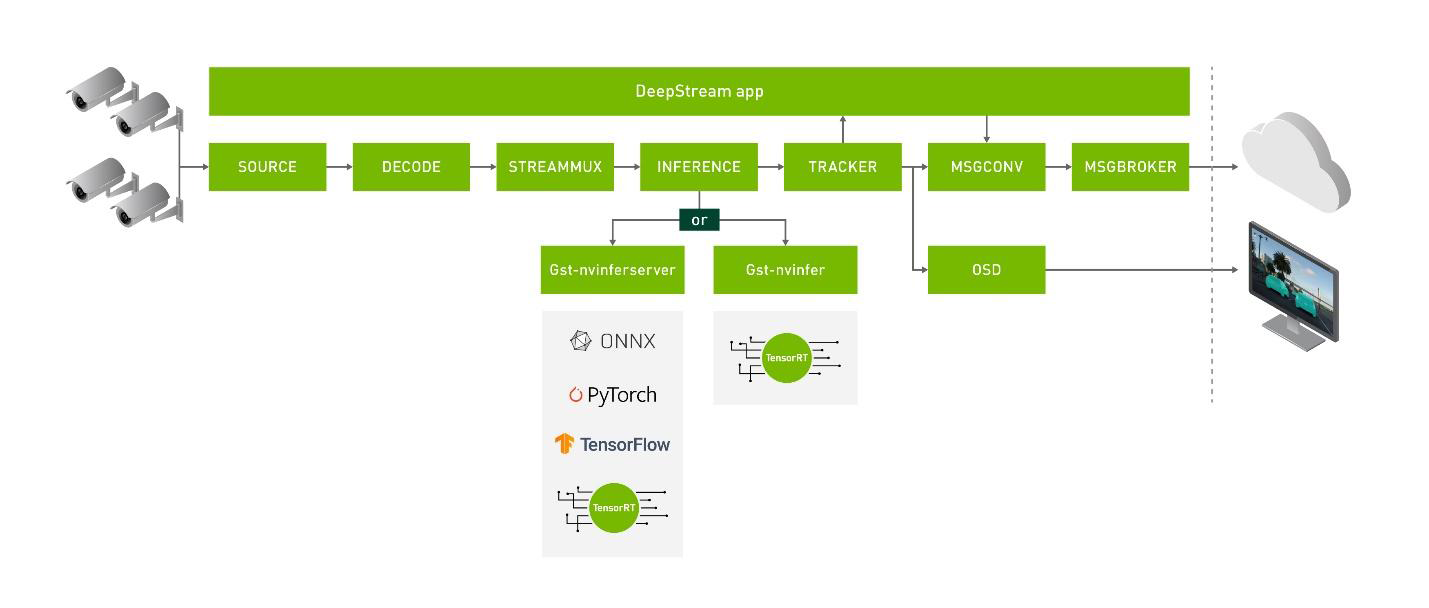 |
|---|
| Complete Deepstream Module |
One of the main module that slows down the system is the detector/ classifier, due to no of matrix operations that it has to do on the GPU, we need a better way to do it. This is where Nvidia Tao and TensorRT comes in.
TensorRT
TensorRT is the heart of the Deepstream. You can take TRTorch to convert your pytorch model to TensorRT. TensorRT is a platform for high-performance deep learning inference. It includes a deep learning inference optimizer and runtime that delivers low latency and high-throughput for deep learning inference applications. TensorRT is a C++ library with Python bindings that allows developers to maximize GPU utilization and extract maximum performance from NVIDIA GPUs. TensorRT provides a Python API that allows developers to integrate deep learning inference into their applications. TensorRT is available in the NVIDIA Deep Learning SDK and is supported on NVIDIA Jetson, NVIDIA DGX, and NVIDIA T4 GPUs.
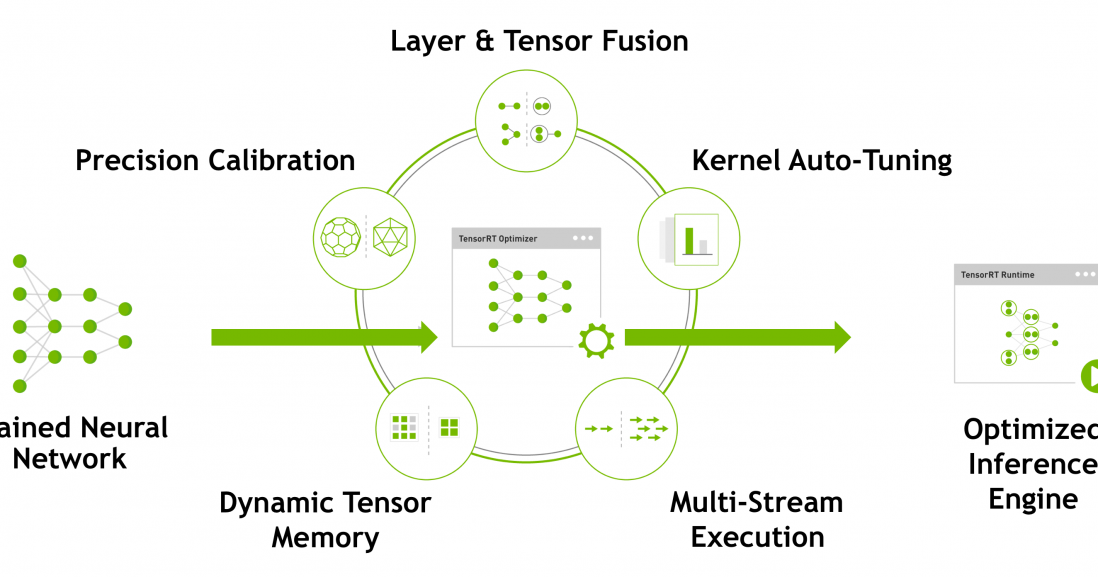 |
|---|
| TensorRT Module |
Precision Calibration: for Medical Imaging use fp64. for almost all other applications you can degrade it fp16 or int8, so that we can run the model at higher fps
Layer and Tensor: Advanxed tech that can do matrix mutiplications at a faster pace, this is where the speed comes from. I am talking about operations like convolutions, max pooling and, stuff like that in deep learning, incase if you find a new operation you can even write one of your own in tensorrt OSS and achieve the same performance the nvidia gives you as a researcher or a hobbyist.
Dynamic Tensor Memory: One need to clean the cache memory once done with operations, this is done by tensorRT, so that you dont have to worry about it.
MultiStream Execution: naive pytorch/tf does have a capability of handling the parallel streams together, nvidia does that for us, so the performace remains almost same all the time.
Kernal autotuning GPU have kernals, these kernals are used to do operations on the GPU, these kernals are optimized for the operations that we do, so that we can achieve the best performance. The engine file is generated based on the gpu you use, so that it can give the best perfomance.
TensorRT makes an engine file in the end which is used by Deepstream to run the inference. Sometime its a tedious process to install things and check, because you can train on an VM( which can have a A100 GPU) and do inference of sample images on local machine GTX series, errors can rise due to different CUDA versions, different TensorRT versions, etc. Deepstream have bindings inside which can do this for you, by giving either a .onnx file or a weights file.
GSTreamer
|  |
|:–:|
| Gstreamer Module |
|
|:–:|
| Gstreamer Module |
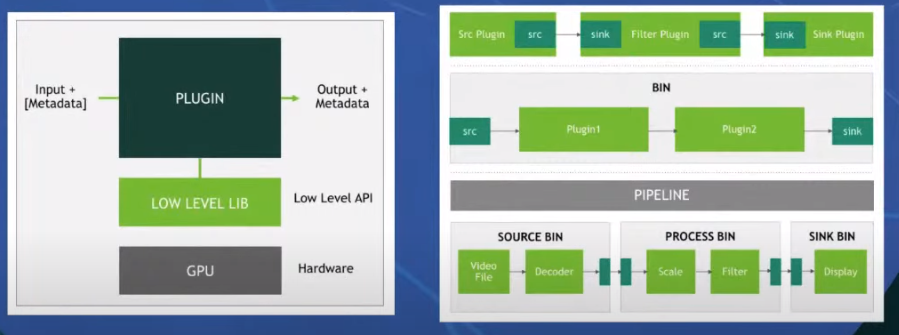
Deepstream gives certain level plugin, lets say you have an image of (254,512,3) and wanted to resize it to(224,224,3), the plugin is loaded and the operation is done in GPU using deeplearning.
Every plugin have a src(source) and a snk(sink). The function of them are analogous to input/output. People like to write code modular, so you make things in sequence.
Bin is a sequence of plugins. Pipeline is a sequence of bins. Pipelines can be used to deal and control things according to the user.
Triton Server
This is better of all for some reason, if the models are not compactable to deepstream.
 |
|---|
| TensorRT Module |
